Numerous technologies are necessary to create a leading customer service organization; however, each technology investment must be scrutinized for its ability to deliver on customer experience (CX) goals.
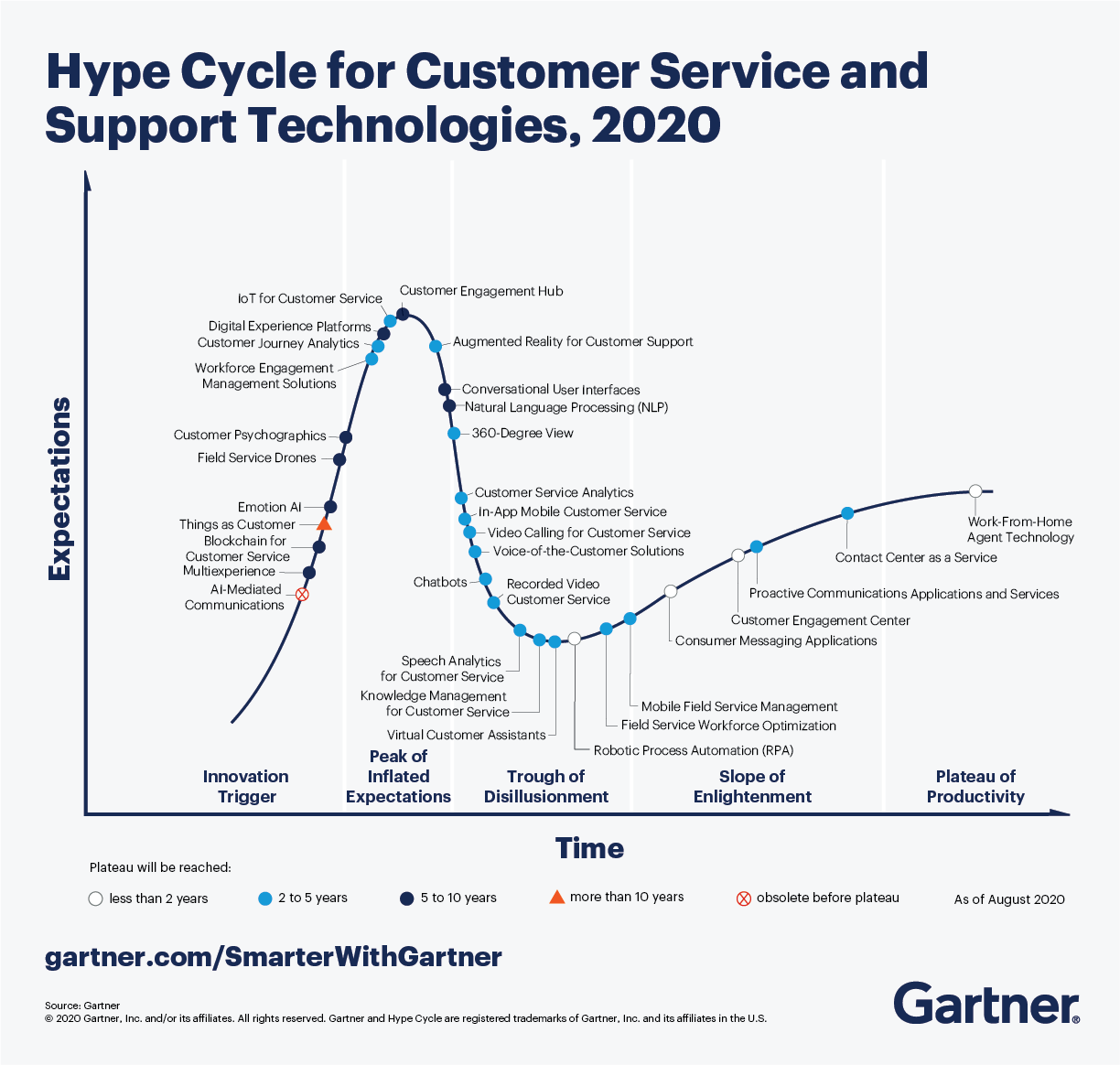
The Gartner Hype Cycle for Customer Service and Support Technologies, 2020 describes the 33 must-watch technologies for supporting customers, evaluating how hyped or how mature the selected technologies are and the business value they could provide.
“Organizations’ customer experience priorities have changed in response to the COVID-19 pandemic,” says Drew Kraus, VP Analyst, Gartner. “As a result, this year’s Hype Cycle encourages service and support leaders to approach the broad range of service and support technologies as an integrated ecosystem of functionality. Then they can better analyze investments that will provide a consistent, effortless, intelligent and personalized customer service experience to meet their CX goals.”
Customer engagement hub
A customer engagement hub (CEH) is an architectural framework that ties multiple systems together to engage customers optimally. It enables proactive and reactive communication as well as personalized, contextual customer engagement, using humans, artificial agents or sensors, across all interaction channels. For example, it can reach and connect all departments to synchronize marketing, sales and customer service processes.
“Operational and technology silos will remain a norm that large enterprises must confront,” says Kraus. “However, a focus on the emerging CEH will foster personalized and consistent engagement with customers, while gaining agreement from both IT and business functions.”
Customer service analytics
Customer service analytics is the combination of interaction analytics (desktop, speech and text), customer journey analytics and next best action analytics that collectively surfaces real-time and historical insight into the customer service experience.
Deploying customer service analytics has the potential to uncover a diverse range of insights that can be used to improve the performance of the operation and its advisors. But it can be challenging to build a business case, because often the insights (and therefore the potential return on investment) won’t be apparent until after the investment is made.
Voice-of-the-customer solutions
Voice-of-the-customer (VoC) solutions combine multiple, traditionally siloed technologies associated with the capture, storage and analysis of direct and indirect customer feedback.
By integrating data from multiple VoC sources, organizations can uncover subtler insights, drive accuracy and ultimately instill more confidence in the actions taken at the levels of both the individual customer (such as an outbound call) and overarching strategy (such as a process change).
This holistic approach ensures that the right insight gets to the right employees at the right time. Overall, these insights can be used to help manage brand perceptions, understand the customer experience and develop future customer engagement strategies.
Chatbots
A chatbot is a conversational interface that uses an app, messaging platform, social network or chat solution for its conversations. Chatbots vary in sophistication from simple, decision-tree-based marketing stunts to implementations built on feature-rich platforms. Already in use in customer service, chatbots played a strategic role in some companies’ responses to COVID-19. This might have an acceleration effect on the technology.
Virtual customer assistants
A virtual customer assistant (VCA) is an application that acts on behalf of an organization to engage, deliver information or act on behalf of a customer. Virtual customer assistants differ from chatbots — they require more infrastructure, have memory and form relationships with customers.
The effective use of a VCA enables organizations to scale the numbers of engagements they can handle, especially in contact centers. The use of a voice-enabled VCA in a kiosk or automated teller machine can alleviate the need for typed interventions and can help create an interesting interaction for nontraditional audiences.