A lot can change in a year. Especially this year. For Boston Dynamics, the past 12 months have brought a number of radical changes traditionally not seen at 30-year-old businesses of its size. It’s a list that includes the first new CEO in the company’s history, wide availability of its first commercial product and, most recently, being acquired by its third owner in seven years.
Of course, no one has ever accused Boston Dynamics of being traditional.
Last week, the Waltham, Massachusetts-based robotics pioneer confirmed earlier rumors that it was being acquired by Hyundai. The South Korean tech giant will be taking an 80% stake in the company, leaving the other 20% or so to its former owner, Softbank Group. The deal, which values the 300-person company at $1.1 billion, is expected to close next June.
“We grew from 100 people to 300 people under SoftBank,” CEO Rob Playter tells TechCrunch. “That took investment. It took encouragement from them to launch a product, launch the products that we had in mind. It was critical. So our mission, which they started us down the path of, is to launch multiple robot products that include mobility, manipulation and vision. And they really gave us power and afterburners to pursue that mission.”
Playter, a longtime Boston Dynamics employee, waves away unfavorable optics around the company’s quick transitions between owners. Each owner served its function for the company’s bottom line — Google offered resources for exploration, SoftBank compelled it to productize and Hyundai will deliver the sort of engineering and manufacturing know-how required to scale up its products.

Image Credits: Boston Dynamics
“Ultimately [SoftBank is] an investment company, and we always expected there to be some kind of an exit,” says Playter. “The question was always when, and when is the right timing? So this isn’t really a surprise to us. And I think they saw and we saw that the time was right as our product launch grew to get a different kind of partner.”
The executive adds that the nature of the company’s interactions with SoftBank were ultimately limited under regulatory restrictions placed on the acquisition by the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS). “Getting through CFIUS will be a closing condition on the Hyundai deal,” he explains.
While SoftBank’s ownership of the company was seen as, at very least, aggressively nudging the company in the direction of commercialization after decades of operating as a research firm, the executive tells TechCrunch that Hyundai largely approved of the company’s existing roadmap. The past two years have certainly brought some profound changes for the company, but Boston Dynamics is still a fairly lean organization, and as such is designed to take a measured approach to the market.
Of the 300 or so employees, between 100 to 120 are currently focused on its first commercial product, Spot. Many of the company’s recent hires are focused on areas like sales, customer service and quality control — relatively unfamiliar terrain for an organization that went more than a quarter-century without releasing its first product. The team focused on its logistics robot, Handle, is significantly smaller, but growing, and will “match or exceed Spot over the course of the next year,” he adds. Handle is, after all, Boston Dynamics’ commercial launch. The company is set to unveil the commercialized version of the box-lifting machine in April. Pilot programs similar to those offered for Spot will follow and sales of the product will start at some point the following year.
The company has already begun to test “proof of concept” models with select partners in real-world warehouses. “These are systems for development that we’re taking onto customer sites to do proof of concept tests,” says Playter. “We’re taking learnings from that to improve the design. In parallel work, we’re designing the for-manufacture version of that robot right now. And first versions of that new generation will come online next summer.”
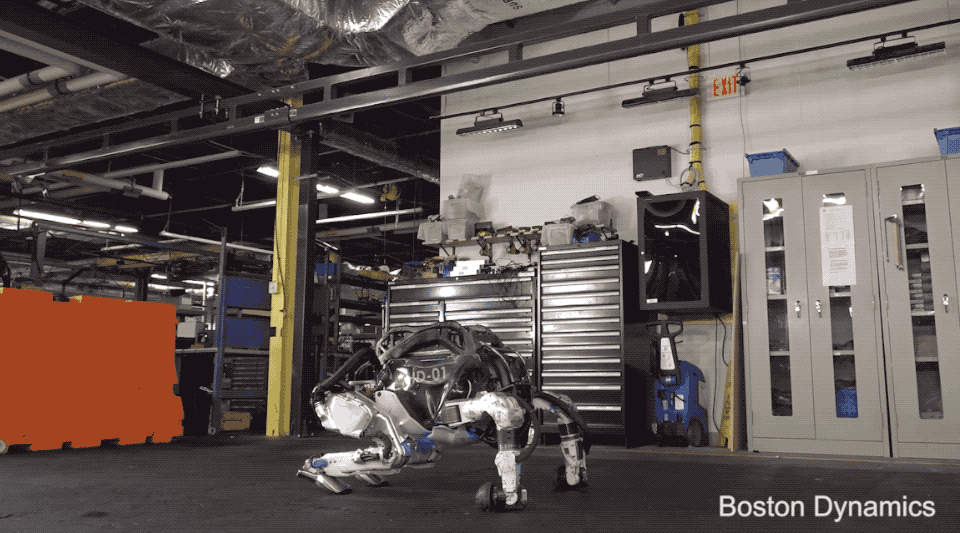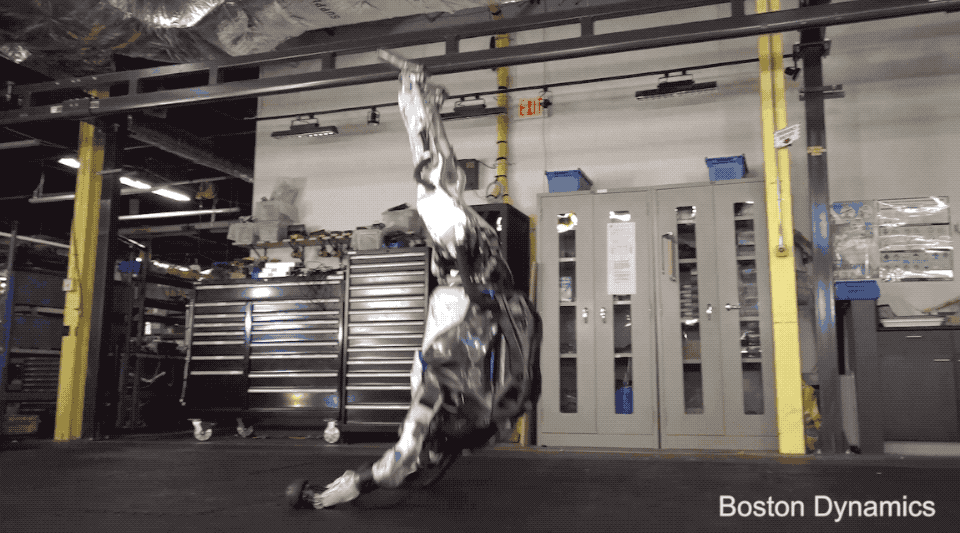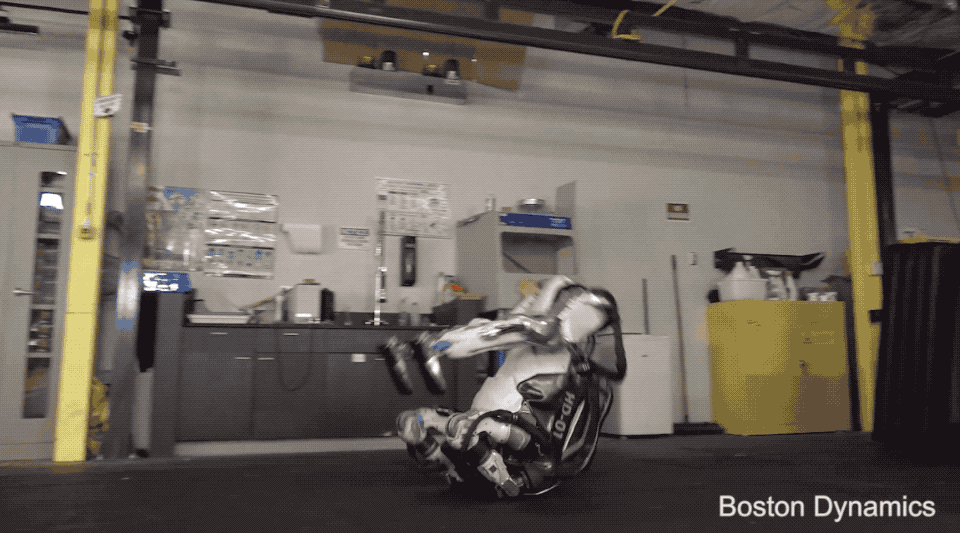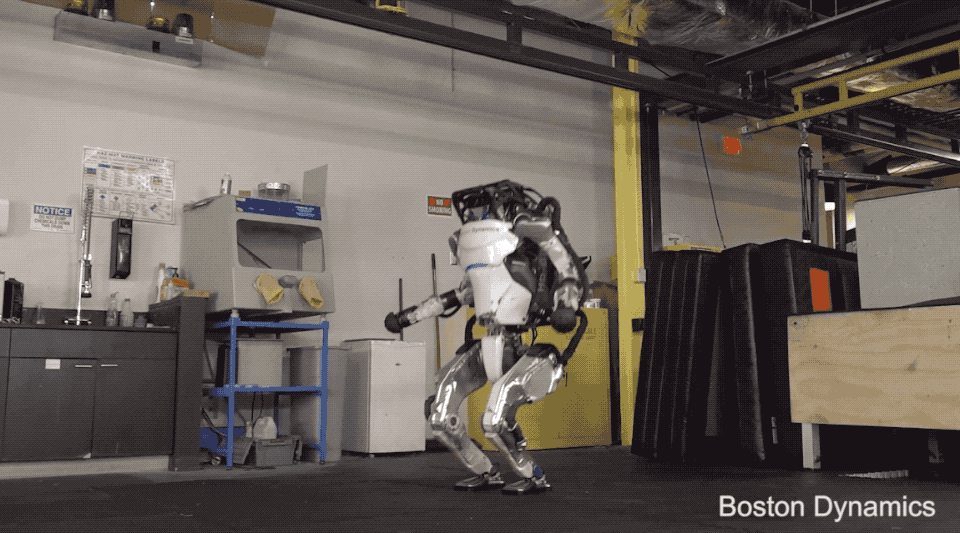
Fulfilment and logistics have already been a hot category for robotics for a number of years, but interest has only grown amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Handle represents a decidedly different to-market approach than Spot, in that respect. A large part of the quadrupedal robot’s pilot program was working with customers and partners to determine which categories had the highest demand for the advanced robotics technology. Demand for Spot hasn’t been huge, but it’s been steady, with the company selling more than 400 million units in the first 15 months.
In-demand applications include deployment in dangerous scenarios like a BP oil rig and a National Grid electric plant. Other more surprising use cases have arisen, as well. Late last year, the ACLU raised concern around video of a Spot robot featured in police training drills, which debuted at our Robotics event back in April. This October, a Spot was seen at a crime scene in Brooklyn. Playter confirmed that the NYPD is one of the company’s customers.
“They have a Spot and were using it, I think, to maintain a safe standoff distance when somebody (a potentially armed suspect) was barricading themselves,” he explains. “So I think getting a camera in and potentially communicating, de-escalating a potentially dangerous situation was the goal there.”
“One of the intended purposes of Spot is to enhance the safety of our customers by removing or providing the opportunity to remove a person from a dangerous environment,” Playter adds. “And that includes public safety officials like the police. And in particular, the Massachusetts State Police have been interested in using Spot in a classic mobile robot application, investigating suspicious packages or potential bombs. So I think these are great applications of robotics and something that we support.”
The next year will also see Boston Dynamics continuing to expand Spot’s available markets. Under the Hyundai banner, the company will likely continue the pace of releases set by Spot and Handle.
“I think something like a robot every couple of years is a pace that we could manage. From clean sheet, we can build a new robot in under a year,” says Playter. “And then you have to go through an iterative process of refining that concept and starting to understand market fit. And so I would look to, I want to stabilize the launch of Spot. There’s already improvements to Spot that we want to be thinking about. So I don’t know if we’re going to go build the next generation of Spot or maybe build the next robot for the next market. And that remains to be seen. We don’t quite have the team that’s big enough to do that just yet.”

The company’s research wing, which focuses on even more bleeding-edge robots like the humanoid Atlas, will also continue under Hyundai’s watch. The company stopped accepting new defense contracts in 2014, shortly after the Google acquisition, but research continues to be a key part of Boston Dynamics’ work.
“[W]e’re developing our own R&D work with Atlas internally,” Playter says. “And so we still use that as a platform to build both advanced hardware and software. We have some exciting things that I think will come out in the near future. We’re going to show you what we’ve been up to, probably in the classic Boston Dynamics home grown video way. I don’t think we have a deadline on when that’s going to come out, but there’s something in the oven.”
Integrating some of Boston Dynamics’ more advanced research into far out Hyundai concepts like the recently announced Ultimate Mobility Vehicle could also be a good fit. “We think the combination of wheels on legs is really interesting. If you recall, we built the first version of Handle with wheels and legs. And so there’s some real synergy there, I think. I think they’re really going to be able to build those vehicles.”




















