Almost exactly a year after Google announced the first developer preview of Android 11, the company today released the first developer preview of Android 12. Google delayed the roll-out of Android 11 a bit as the teams and the company’s partners adjusted to working during a pandemic, but it looks like that didn’t stop it from keeping Android 12 on schedule. As you would expect from an early developer preview, most of the changes here are under the hood and there’s no over-the-air update yet for intrepid non-developers who want to give it a spin.
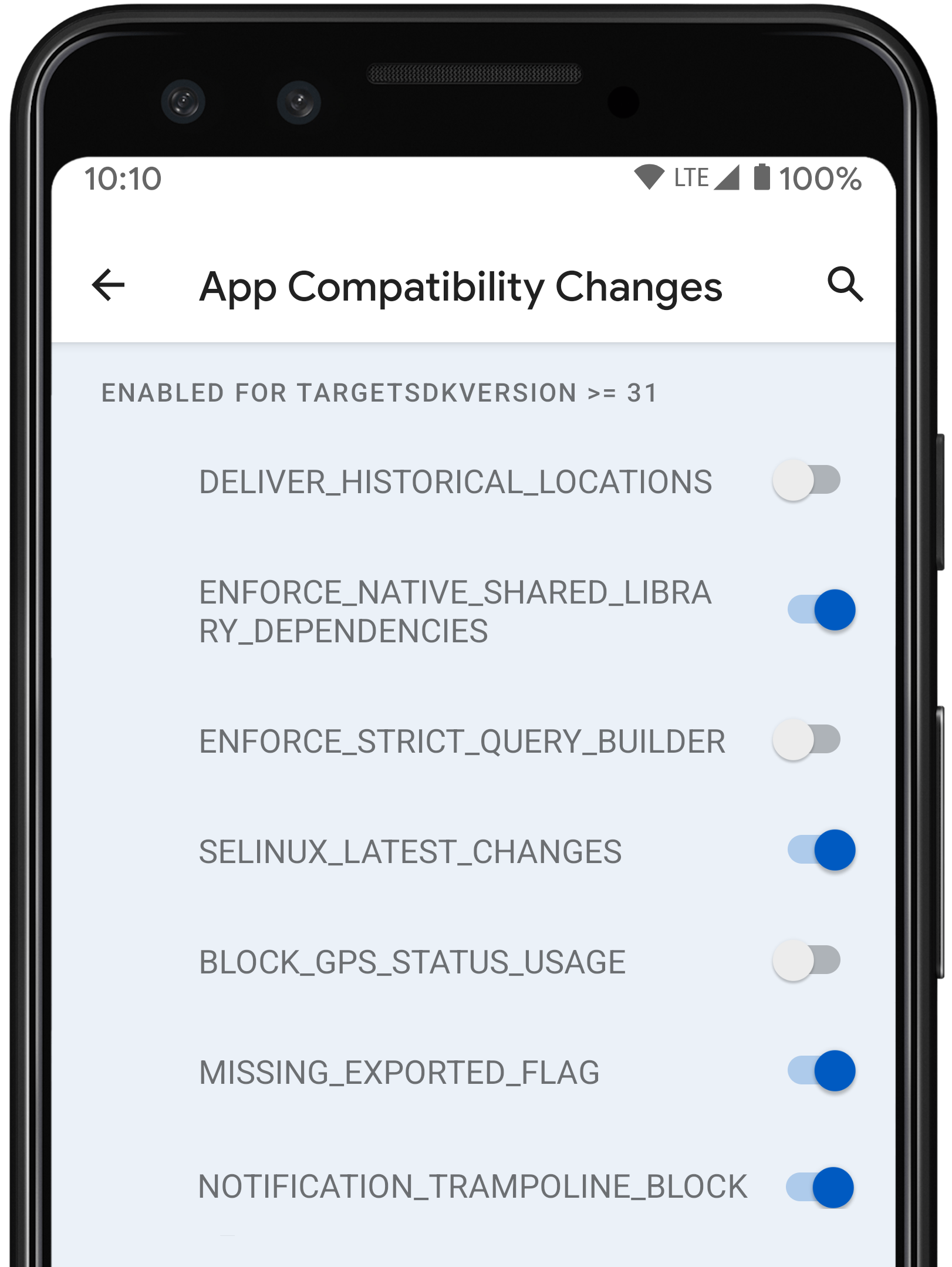
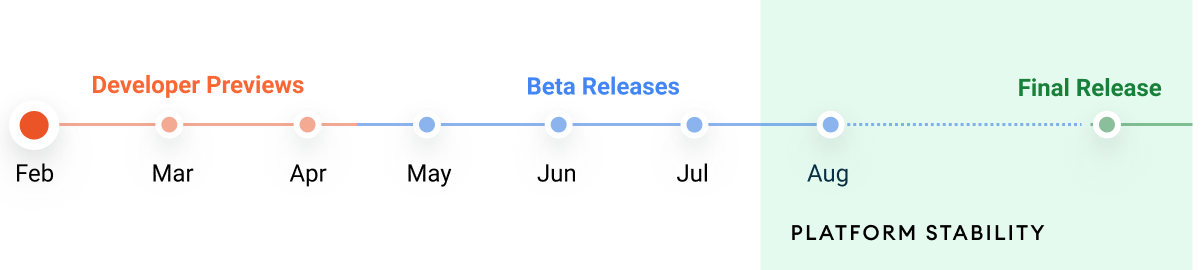
Among the highlights of the release so far — and it’s important to note that Google tends to add more user-facing changes and UI updates throughout the preview cycle — are the ability to transcode media into higher quality formates like the AV1 image format, faster and more responsive notifications and a new feature for developers that now makes individual changes in the platform togglable so they can more easily test the compatibility of their apps. Google also promises that just like with Android 11, it’ll add a Platform Stability milestone to Android 12 to give developers advance notice when final app-facing changes will occur in the development cycle of the operating system. Last year, the team hit that milestone in July when it launched its second beta release.
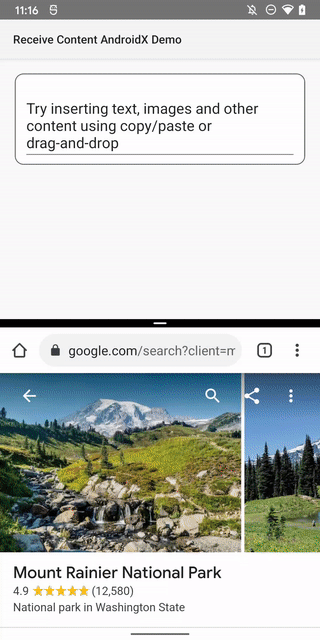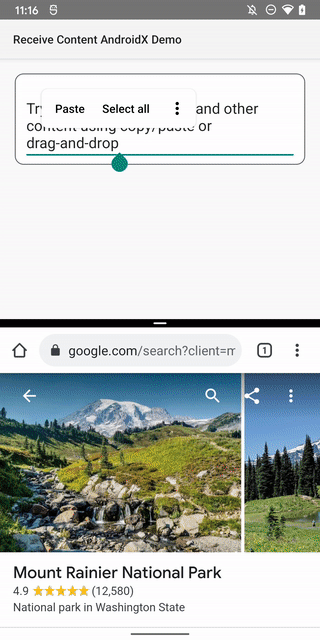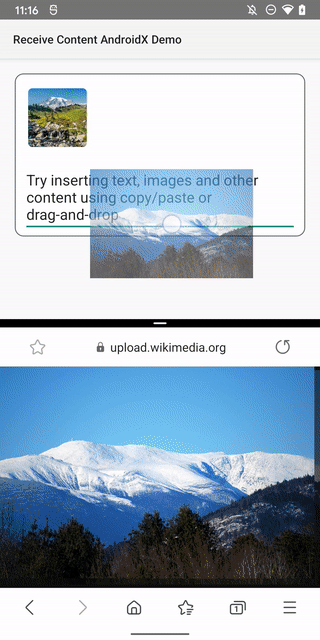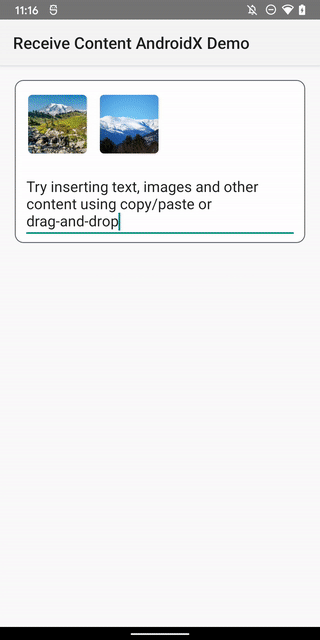
“With each version, we’re working to make the OS smarter, easier to use, and better performing, with privacy and security at the core,” writes Google VP of Engineering Dave Burke. “In Android 12 we’re also working to give you new tools for building great experiences for users. Starting with things like compatible media transcoding, which helps your app to work with the latest video formats if you don’t already support them, and easier copy/paste of rich content into your apps, like images and videos. We’re also adding privacy protections, refreshing the UI, and optimizing performance to keep your apps responsive.”
Obviously, there are dozens of developer-facing updates in Android 12. Let’s look at some in detail.
For the WebView in Android 12, Google will now implement the same SameSite cookie behavior as in Chrome, for example. Last year, the company slowed down the roll-out of this change, which makes it harder for advertisers to track your activity across sites, in Chrome, simply because it was breaking too many sites. Now, with this feature fully implemented in Chrome, the Android team clearly feels like it, too, can implement the same privacy tools in WebView, which other apps use to display web content, too.
As for the encoding capabilities, Burke notes that, “with the prevalence of HEVC hardware encoders on mobile devices, camera apps are increasingly capturing in HEVC format, which offers significant improvements in quality and compression over older codecs.” He notes that most apps should support HEVC, but for those that can’t, Android 12 now offers a service for transcoding a file into AVC.
In addition, Android 12 now also supports the AV1 Image File Format as a container for images and GIF-like image sequences. “Like other modern image formats, AVIF takes advantage of the intra-frame encoded content from video compression,” explains Burke. “This dramatically improves image quality for the same file size when compared to older image formats, such as JPEG.”
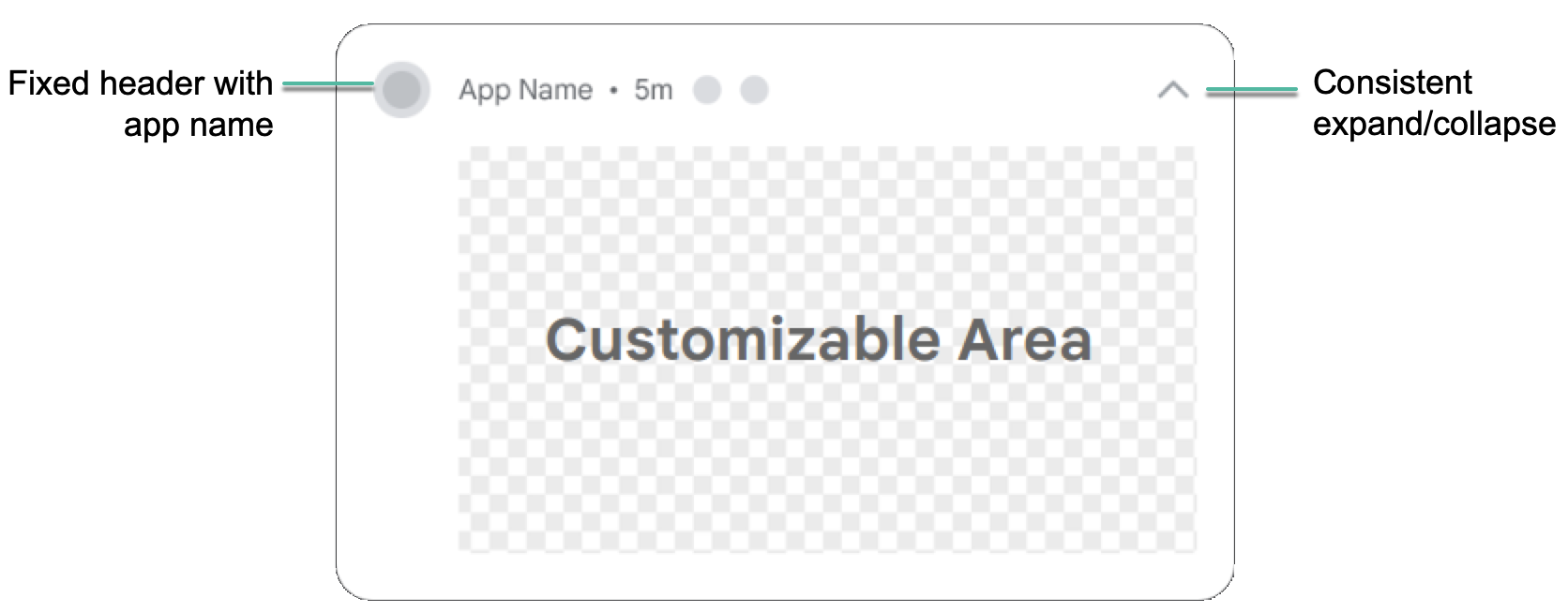
As with every Android release, Google also continues to tinker with the notification system. This time, the team promises a refreshed design to “make them more modern, easier to use, and more functional.” Burke calls out optimized transitions and animations and the ability for apps to decorate notifications with custom content. Google now also asks that developers implement a system that immediately takes users from a notification to the app, without an intermediary broadcast receiver or service, something it recommended before.
Android 12 will now also offer better support for multi-channel audio with up to 24 channels (a boon for music and other audio apps, no doubt), spatial audio, MPEG-H support, and haptic-coupled audio effects with the strength of the vibration and frequency based on the audio (a boon for games, no doubt). There’s also improved gesture navigation and plenty of other optimizations and minor changes across the operating system.
Google also continues to drive its Project Mainline forward, which allows for an increasing number of the core Android OS features to be updated through the Google Play system — and hence bypasses the slow update cycles of most hardware manufacturers. With Android 12, it is bringing the Android Runtime module into Mainline, which will then let Google push updates to the core runtime and libraries to devices. “We can improve runtime performance and correctness, manage memory more efficiently, and make Kotlin operations faster – all without requiring a full system update,” Burke says. “We’ve also expanded the functionality of existing modules – for example, we’re delivering our seamless transcoding feature inside an updatable module.”
You can find a more detailed list of all of the changes in Android 12 here.
Developers who want to get started with bringing their apps to Android 12 can do so today by flashing a device image to a Pixel device. For now, Android 12 supports the Pixel 3/3 XL, Pixel 3a/3a XL, Pixel 4/4 XL, Pixel 4a/4a 5G and Pixel 5. You can also use the system image in the Android Emulator in Google’s Android Studio.