Researchers at Kaspersky’s Security Services shared their predictions for next year’s trending cyberthreats that large businesses and government structures should prepare for. They include cybercriminals using media to blackmail organizations, reporting alleged data leaks, and purchasing initial access to previously compromised companies on the darknet. Other threats involve the rise of the Malware-as-a-Service model and attacks via the cloud. This report is a part of Kaspersky Security Bulletin (KSB) – an annual series of predictions and analytical reports on key shifts within the cybersecurity world.
Hacker attacks repeatedly harm individuals, damage corporations, and can even threaten entire countries, and not just financially. The media routinely report incidents and data breaches that become publicly accessible on the dark web. This threatens not only personal privacy, but companies’ reputations. As part of the Kaspersky Security Bulletin, the Kaspersky Security Services experts – a group that helps businesses enhance existing security systems and equips them to meet new threats – has reviewed the threats that will be relevant to big business and the government sector in the coming year.
Blackmailing: hackers’ public posts with a countdown to data leaks
Ransomware actors are increasingly posting about new successful hacking incidents perpetrated on businesses in their blogs – the number of such publications grew in 2022. The peak number exceeded 500 per month, and this occurred several times between the end of 2021 and the first half of 2022. This compares to 200 to 300 posts observed monthly by experts at the beginning of 2021. Extortionists were also active at the end last year: in September and November, Kaspersky’s Digital Footprint Intelligence tracked roughly 400 and 500 posts, respectively.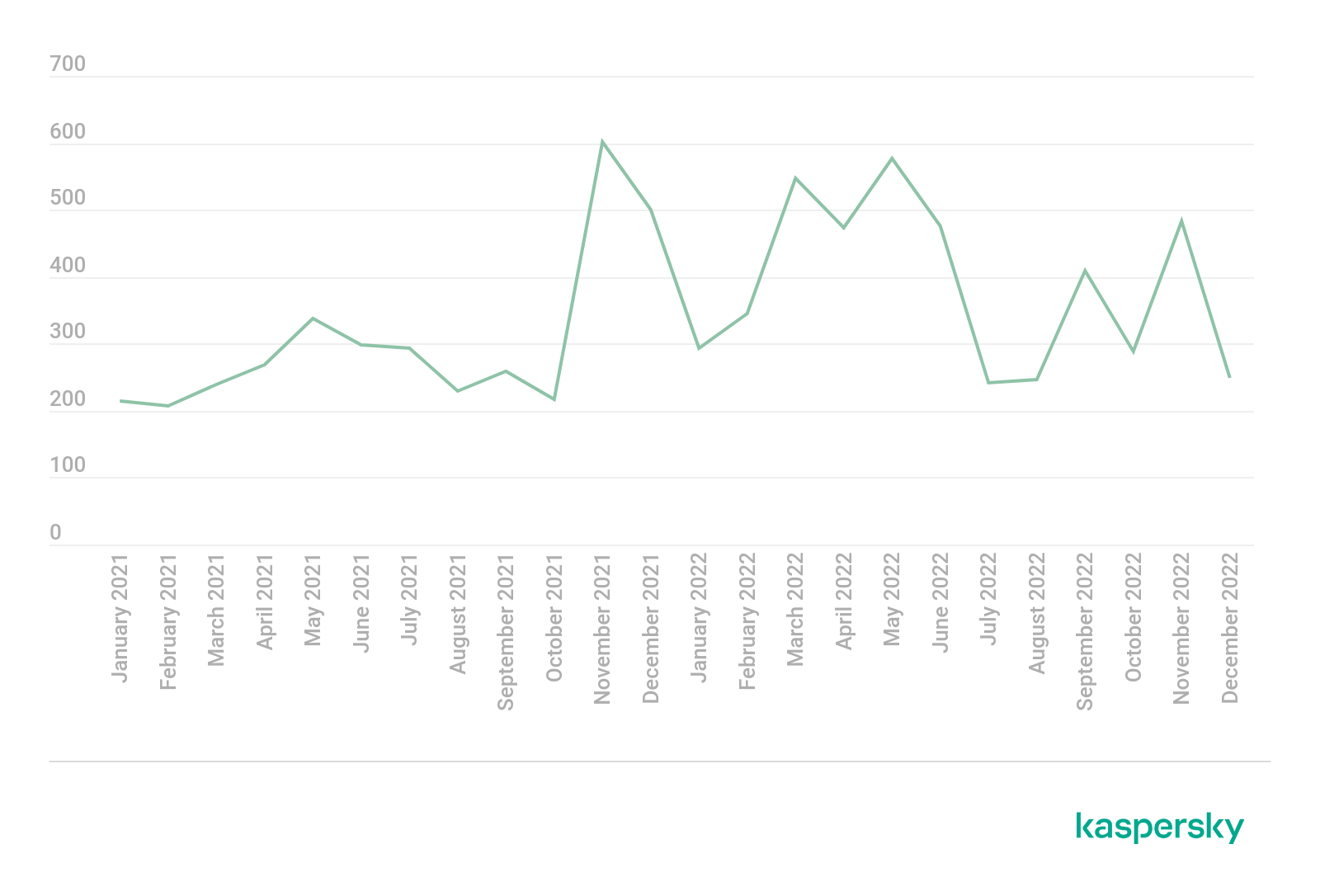
Changes in the number of ransomware blog posts in 2021–2022. The statistics contain data on sites that are covered by the Digital Footprint Intelligence monitoring system
Cybercriminals used to reach the victim directly, but now they post about the security breach in their blogs immediately, setting a countdown timer to the publication of the leaked data instead of privately demanding a ransom. This dark trend will continue developing in 2023 because this tactic benefits cybercriminals whether the victim pays up or not. Data is often auctioned, with the closing bid sometimes exceeding the demanded ransom.
Cybercriminals post about fake leaks to boost their reputation
Blog posts about extortion attract media attention, and some lesser-known actors might take advantage of this in 2023, by claiming they have allegedly hacked a company. Whether the hack actually happened or not, a leak report might hurt the business. The key to staying safe is to identify these messages in a timely fashion and initiate a response process similar to that used in information security incidents.
More personal data leaks, corporate emails at risk
The experts expect the trend of personal data leaks to continue into 2023. Even though it directly influences individuals’ privacy, corporate cybersecurity is put at risk as well. People often use work email addresses to register with third-party sites, which can be exposed to a data leak. When sensitive information such as email addresses become publicly accessible, it may invoke the interest of cybercriminals and trigger discussions of potential attacks on the organization on darknet websites; additionally, the data can be used for phishing and social engineering.
Malware-as-a-service, attacks via cloud and compromised data sourced on the dark web
Experts also expect ransomware attacks to grow in similarity due to the rise of malware-as-a-service (MaaS) tools. The complexity of attacks will increase, meaning automated systems won’t be sufficient to ensure complete security. Furthermore, cloud technology will become a popular attack vector, as digitalization brings increased cybersecurity risks with it. Apart from that, cybercriminals will tap dark web sites more often in 2023 to purchase access to previously compromised organizations.
“The threat landscape is rapidly developing, and companies are being forced to adapt quickly. In order to protect a large business or a government agency from trending threats, it is necessary to monitor the digital footprint of the organization. It is important to be prepared to investigate and respond to incidents, since it is not always possible to stop attackers before they penetrate a perimeter. However, preventing an attack development and limiting potential damage is an absolutely feasible task,” said Anna Pavlovskaya, Security Services Analyst at Kaspersky.
























