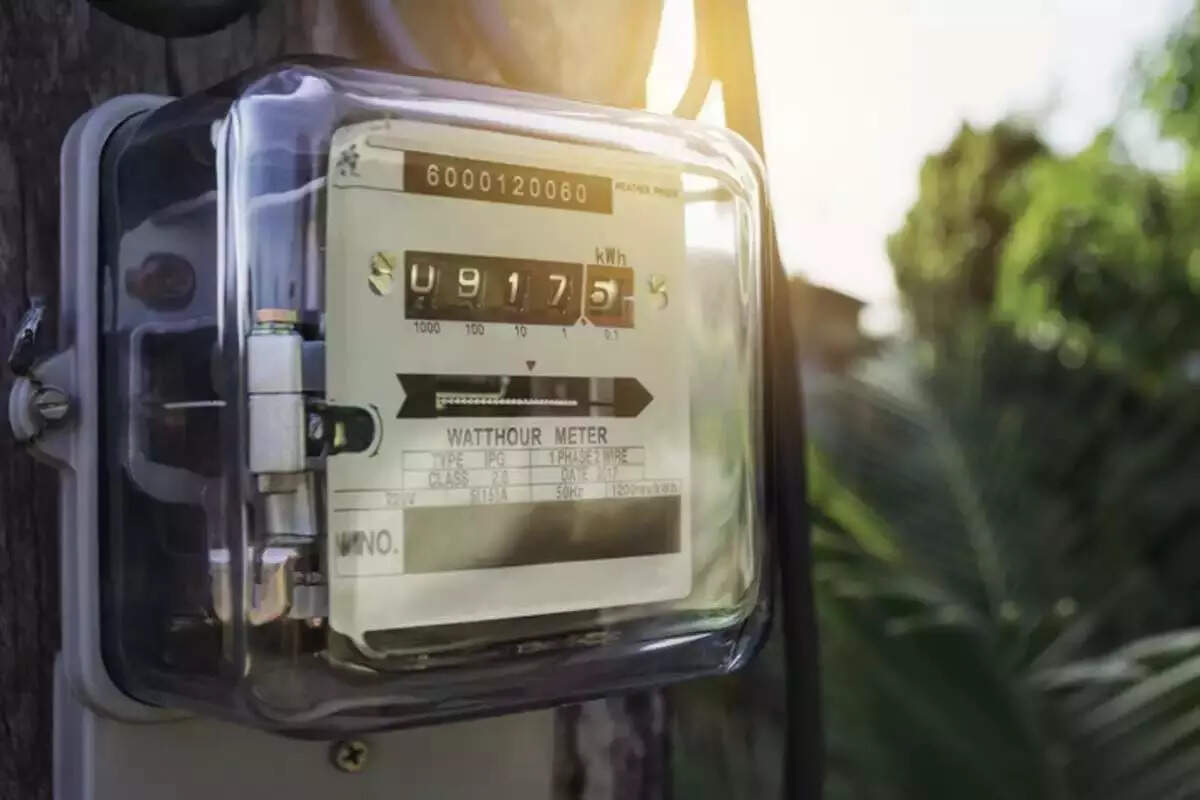
Lately, smart meters have been gaining traction for their capacity to transform electricity supply services in India by bringing in reliability and transparency in the sector. They serve a pivotal function in transforming distribution utilities by reducing billing and collection inefficiencies, providing near real time data for analytics and strategic input for minimising pilferage, planning and operation of the distribution grid.
From analog meters to conventional electronic meters to new smart meters, metering technologies have evolved from meters as individual commodity to metering system including IT and prepayment. Smart meters have transformed how utilities and consumers track and control energy usage, extending convenience and accuracy.India’s energy landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, fuelled by the widespread adoption of digitisation. With the introduction of the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme, aimed at revitalizing distribution utilities, and innovative initiatives like the PM Surya Ghar Yojna, smart meters will bring in the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability in India’s power sector.
The country’s smart meter market was evaluated at US$ 219.7 million in 2023 and is anticipated to reach a market size of US$ 3,179.5 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 34.57 % for the duration of the predicted period 2024-2032.
Schemes and Growing Importance of Electricity
As part of the Ministry of Power (MoP), Government of India (GoI) targets to transition from conventional electronic metering to smart prepay metering, an outlay of INR 1.35 trillion has been sanctioned under Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS), was announced to replace 250 million static energy meters with smart prepaid meters along with end-to end metering at all voltage levels. RDSS provides much needed flexibility in project implementation, as it allows utilities and states to custom tailor the projects to their unique needs. By promoting innovation and collaboration, these schemes encourage the development of solutions that are both effective and sustainable.The active industry participation and contribution of over 45 manufacturers in this initiative is a testament to its potential impact. With a diverse array of players bringing their expertise to the table, smart meter technology in India is poised for rapid advancement. This not only fosters healthy competition but also brings in the best of quality standards, making these solutions more accessible to utilities and consumers alike.
A recent study showed that as on date, the Indian state of Bihar, with ~3.2 million smart meters, had the highest number of smart meters installed across the country. This was followed by Uttar Pradesh and Haryana.
Smart metering technology holds significant potential and has a substantial impact. Utilizing digital technology, smart metering facilitates a bidirectional flow of electricity and information, offering an innovative and comprehensive solution. Its effectiveness and reliability in managing electricity consumption, as well as demand and supply, have been demonstrated over years through multiple global implementations.
Smart meters play a crucial role in real-time monitoring and data insights, revolutionizing the way consumers engage with their energy usage. By providing constant updates on consumption patterns, these devices empower individuals to identify energy-intensive appliances or habits promptly. This real-time feedback fosters behavioural changes and enhances consumer awareness, encouraging actions like turning off lights and adjusting thermostats for energy conservation.
Smart metring provides a lot more than just efficient billing and optimising opex on meter reading and billing. Metering data with right analytics will play a pivotal role in managing grid complexities due to extensive RE penetration, distributed generation, ancillary services and e-mobility. It will also contribute in peak load management and demand response by end consumer inclusion.
Also, with right mix of Time of day (ToD), Time of use (ToU) tariff along with prepay metering utilities are better equipped to cater need of the hour for sustainability.
Moreover, smart meters bolster conservation efforts by incentivizing efficient practices and promoting a culture of sustainability. Armed with detailed data about their energy usage, consumers can make informed decisions to cut back and save, contributing to long-term energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Smart meters also present some challenges. Implementing smart meters presents a dual challenge: balancing the benefits of enhanced energy management with the need to address privacy and security concerns. While smart meters provide invaluable insights into energy consumption patterns, consumers rightfully demand assurances that their personal data remains safeguarded. This necessitates robust measures to protect privacy while harnessing the potential of smart technology.
The deployment of smart meters entails significant infrastructure upgrades and associated costs. It’s not merely a matter of installing new devices; it involves modernizing existing systems and investing in upskilling and deployment logistics. As utilities navigate these challenges, they must strike a delicate balance between innovation and affordability, ensuring that the benefits of smart meters are accessible to all while mitigating the financial burden on consumers and providers alike.
These challenges will overcome with time. The successful implementation of a smart metering project hinges on meticulous planning and execution. Seamless IT integration, robust cybersecurity measures, and revisiting tariff structures are paramount. Additionally, standardizing procedures and prioritizing consumer engagement through awareness campaigns and user-friendly applications are vital for its success.
It is imperative to understand that numerous factors significantly influence the overall operational costs of the AMI stack, and managing these factors and their intricate connections is pivotal in establishing a cost-effective smart meter project. Among the critical elements, several hidden costs emerge during AMI projects, including handling exceptions, restructuring business processes, time required for commissioning, costs related to consumer services, expenses linked to truck rolls, and unforeseen expenses for defective meters. Recognizing and managing these factors for Total cost of ownership is key in ensuring the efficiency and financial viability of the smart meter projects.
", -->
Source Link