Parents with kids stuck learning at home during the pandemic have had to look for alternative activities to promote the hands-on learning experiences kids are missing out on due to attending class virtually. The New York-based educational technology startup Thimble aims to help address this problem by offering a subscription service for STEM-based projects that allow kids to make robotics, electronics and other tech using a combination of kits shipped to the home and live online instruction.
Thimble began back in 2016 as Kickstarter project when it raised $300,000 in 45 days to develop its STEM-based robotics and programming kits. The next year, it then began selling its kits to schools, largely in New York, for use in the classroom or in after-school programs. Over the years that followed, Thimble scaled its customer base to include around 250 schools across New York, Pennsylvania, and California, who would buy the kits and gain access to teacher training.
But the COVID-19 pandemic changed the course of Thimble’s business.
“A lot of schools were in panic mode. They were not sure what was happening, and so their spending was frozen for some time,” explains Thimble co-founder and CEO Oscar Pedroso, whose background is in education. “Even our top customers that I would call, they would just give [say], ‘hey, this is not a good time. We think we’re going to be closing schools down.”
Pedroso realized that the company would have to quickly pivot to begin selling directly to parents instead.
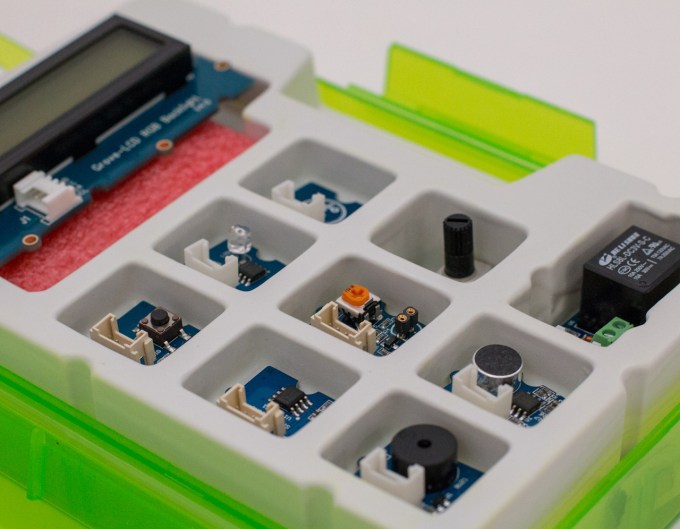
Image Credits: Thimble
Around April, it made the shift — effectively entering the B2C market for the first time.
The company today offers parents a subscription that allows them to receive up to 15 different STEM-focused project kits and a curriculum that includes live instruction from an educator. One kit is shipped out over the course of three months, though an accelerated program is available that ships with more frequency.
The first kit is basic electronics where kids learn how to build simple circuits, like a doorbell, kitchen timer and a music composer, for example. The kit is designed so kids can experience “quick wins” to keep their attention and whet their appetite for more projects. This leads into future kits like those offering a Wi-Fi robot, a little drone, an LED compass that lights up, and a synthesizer that lets kids become their own D.J.
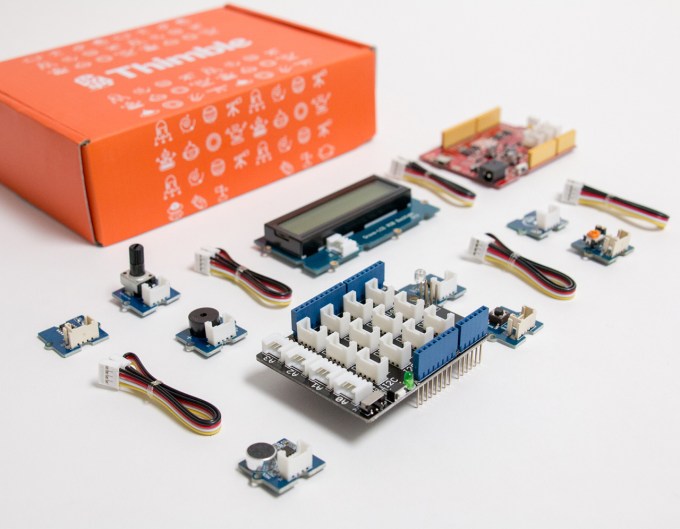

Image Credits: Thimble
While any family can use the kits to help kids experience hands-on electronics and robotics, Pedroso says that about 70% of subscribers are those where the child already has a knack for doing these sorts of projects. The remaining 30% are those where the parents are looking to introduce the concepts of robotics and programming, to see if the kids show an interest. Around 40% of the students are girls.
The subscription is more expensive than some DIY projects at $59.99/per month (or $47.99/mo if paid annually), but this is because it includes live instruction in the form of weekly 1-hour Zoom classes. Thimble has part-time employees who are not just able to understand teach the material, but can do so in a way that appeals to children — by being passionate, energetic and capable of jumping in to help if they sense a child is having an issue or getting frustrated. Two of the five teachers are women. One instructor is bilingual and teaches some classes in Spanish.
During class, one teacher instructs while a second helps moderate the chat room and answer the questions that kids ask in there.
The live classes will have around 15-20 students each, but Thimble additionally offers a package for small groups that reduces class size. These could be used by homeschool “pods” or other groups.
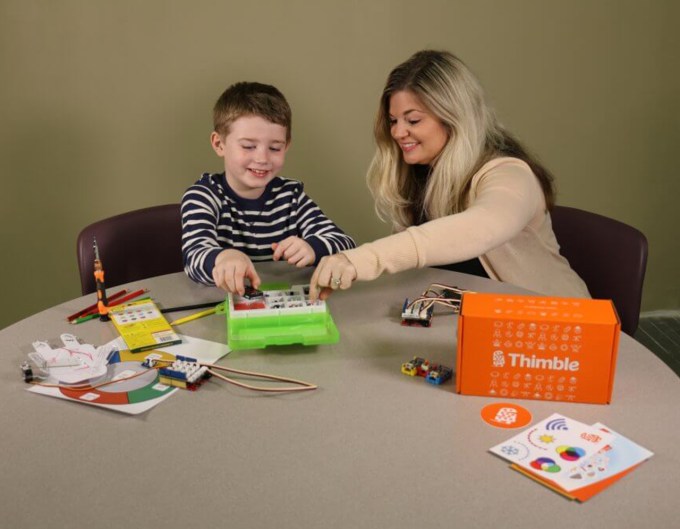

Image Credits: Thimble
“We started hearing from pods and then micro-schools,” notes Pedroso. “Those were parents who were connected to other parents, and wanted their kids to be part of the same class. They generally required a little bit more attention and wanted some things a little more customized,” he added.
These subscriptions are more expensive at $250/month, but the cost is shared among the group of parents, which brings the price down on per-household basis. Around 10% of the total customer base is on this plan, as most customers are individual families.
Thimble also works with several community programs and nonprofits in select markets that help to subsidize the cost of the kits to make the subscriptions more affordable. These are announced, as available, through schools, newsletters, and other marketing efforts.
Since pivoting to subscriptions, Thimble has re-established a customer base and now has 1,110 paid customers. Some, however, are grandfathered in to an earlier price point, so Thimble needs to scale the business further.
In addition to the Kickstarter, Thimble has raised funds and worked on the business over the year with the help of multiple accelerators, including LearnLaunch in Boston, Halcyon in D.C., and Telluride Venture Accelerator in Colorado.
The startup, co-founded by Joel Cilli in Pittsburgh, is now around 60% closed on its seed round of $1 million, but isn’t announcing details of that at this time.



